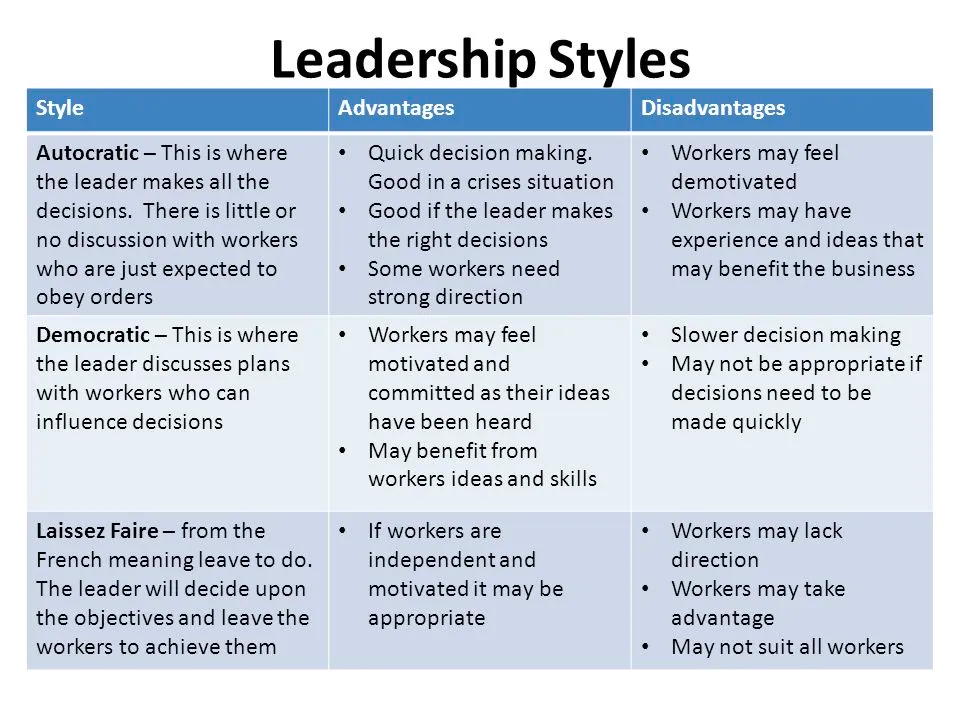
BUSINESS AND LEADERSHIP PHYSCOLOGY
LEADERSHIP
Shavhekha A/P Santhira Sekaran
SCPG 2000001
Introduction
Leadership is a concept, which is put into operation by the individuals in their personal and professional lives. In order to implement this concept in an effective and worthwhile manner, the individuals need to acquire an understanding in terms of meaning and significance of leadership
A mind map is a diagram used to visually organise information. A mind map is hierarchical and shows relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often created around a single concept, drawn as an image in the centre of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those.
Qualities of a leader
GOAL ORIENTED
COURAGE
LEADERSHIP
QUALITIES
High Ethics
PASSION
Honest
INTERGRITY
Responsibe
Focus
PRIORTISES
Falling Action
New Story Mind Map by Dexter Cook | www.po-tech.com
PROCESSES & LATEST DEVELOPEMENT IN RESEARCH
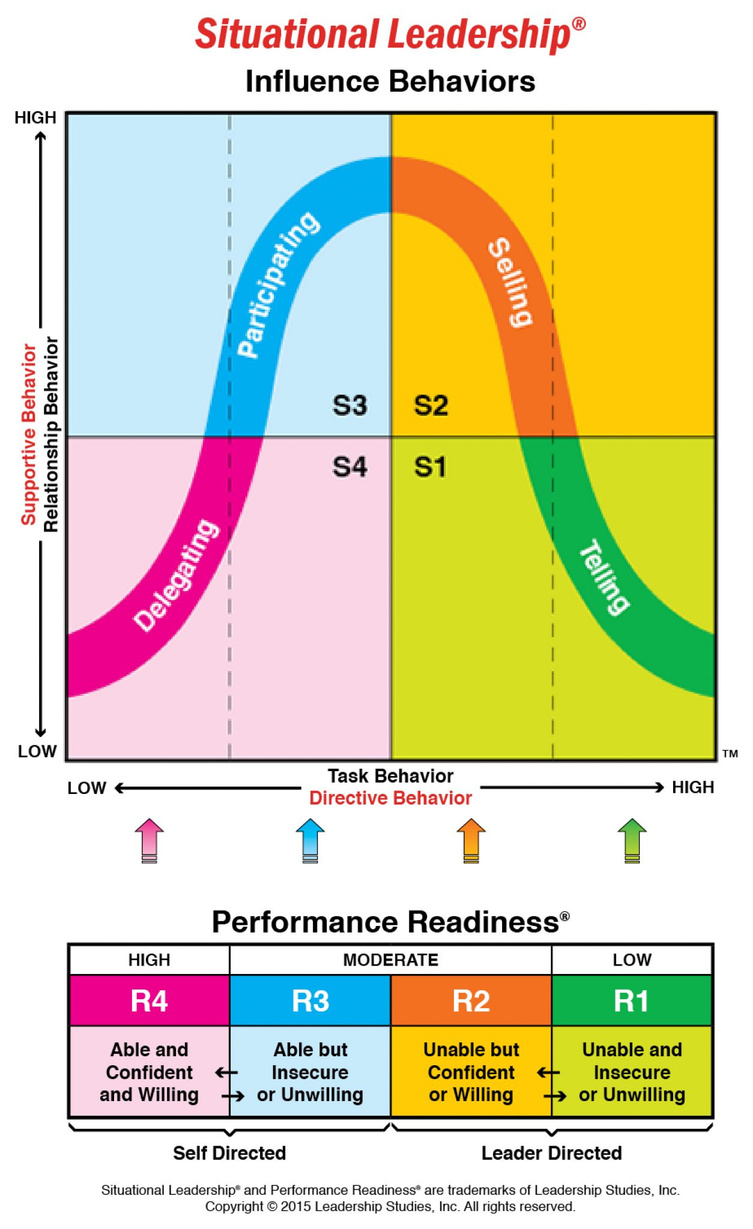
SITUATIONAL LEADERSHIP THEORY
LEADER MEMBER EXCHANGE (LMX) THEORY
VROOM YETTON MODEL
- Developed by HERSEY AND BLANCHARD ( 1998)
- This approach to leadership suggests the need to match two key elements appropriately: the leader’s leadership style and the followers’ maturity or preparedness levels.
- POSTULATED THAT A LEADER TYPICALLY USES ONE OF FOUR BEHAVIORAL STYLES : TELLING, SELLING, PARTICIPATING, DELEGATING.
- Those styles are operationally defined by :
1.Task / Directive BEHAVIOUR
2.Relationship/Supportive Behavior
SITUATIONAL LEADERSHIP THEORY
SITUATIONAL LEADERSHIP THEORY
- Task/Directive Behavior – the extent to which the leader tells the follower what to do, how to do it, where it needs to be done and when it needs to be completed
- Relationship/Supportive Behavior – the extent to which the leader engages in open dialog with the follower, actively listens and provides recognition/reinforcement for task-related progress
Selling
Selling addresses the follower who has developed some competence with an improved commitment. The follower is not convinced yet, but is open to becoming cooperative and motivated.
Telling is the lowest level of leadership style.
This is a very leader-driven stage.
TELLING
Participating
Participating addresses the follower who is now competent at the job, but remains somewhat inconsistent and is not yet fully committed. The follower may be uncooperative or performing as little work as possible, despite their competence with the tasks
This is a very follower-driven, relationship-focused stage.
Delegating
Delegating is the ultimate goal: a follower who feels fully empowered and competent enough to take the ball and run with it, with minimal supervision. The follower is highly competent, highly committed, motivated, and empowered.
This is a very follower-driven stage.
- Developed BY DANSEREAU, GREEN, AND HAGA ( 1975 )
- POSTULATED ORIGINALLY CALLED VERTICAL DYAD LINKAGE ( VDL ) THEORY
follower
leader
DYADIC RELATIONSHIP
LEADER MEMBER EXCHANGE (LMX) THEORY
- LEADERS DEVELOP DIFFERENT ROLES AND RELATIONSHIP WITH THE PEOPLE UNDER THEM AND THUS ACT DIFFERENTLY WITH OTHER SUBORDINATES.
- The theory states that all relationships between managers and subordinates go through three stages. These are:
- Role-Taking.
- Role-Making.
- "Routinization."
- SUBORDINATES FALL INTO TWO GROUPS
- IN-GROUP : CHARACTERISED BY A HIGH QUALITY RELATIONSHIP WITH THE LEADER
- OUT- GROUP : CHARACTERIZED BY A LOW QUALITY RELATIONSHIP WITH THE LEADER
VROOM YETTON MODEL
- Originally developed by Victor Vroom and Philip Yetton in their 1973 book, "Leadership and Decision Making."
- No single decision-making process fits every scenario.
- Before you start using the model, you'll need to consider these three factors:
- Decision quality – Sometimes, making the "right" decision is critical, and you'll need to use a large number of resources (people, time, information, and so on) to ensure that the action you take has been well thought through and is of high quality.
- Team commitment – Some of your decisions will have a major impact on your team, while others will go unnoticed. When a decision will likely impact your team, it's best to use a collaborative process. This will improve the quality of the decision, and you'll likely deliver a successful result faster.
3. Time constraints – When the issue at hand isn't time sensitive, you have more "space" to research your options and to include others, which will help to boost the quality of your decision. If your time is limited, however, it may not be feasible to include others or to undertake thorough research.

Challenges
Discussions
5 DIFFERENT ROLES IN LEADERSHIP
01
02
03
04
04
The Motivator
The Mentor
The Learner
The Communicator
The Navigator
Motivation can vary from person to person. What motivates you? Is it money, time off or recognition? The motivator influences others to act in an advantageous manner. This could take form in recognition for excellent work.
Being guided in the right direction is essential to success. A mentor provides the mentee with the foundation to be successful. This type of leader is the perfect asset to have when reaching new heights in any area of life.
Always aim to be better person today than you were yesterday! The learner is someone who constantly develops their knowledge, skills and abilities to help the organization achieve its strategic goals. Lifelong learning is crucial to sustainability.
Being a good communicator is an important skill set to have in all areas of life. The communicator is the type of leader that listens to incoming messages effectively and articulates what being stated to others in an understandable, concise manner.
Actions are aimed to support missions. Constructing specific objectives steers the vessel in the right direction. The navigator acts as a compass. This leader creates the vision for the organization to advance toward its mission.
Conclusion
- There is a common belief that leadership is vital for effective organizational and societal functioning and success.
- Antonakis et al. (2004) note that because of the complex nature of leadership, a specific and widely accepted definition of leadership does not exist and might never be found.
- However, we can conclude that leadership is the ability to direct a group of people in realising a common goal. This is done by people applying their leadership attributes. Leaders create commitment and enthusiasm amongst followers to achieve goals. Leadership is achieved through interaction between leader, follower and environment.